Whether in communications, surveillance, or industrial settings, telescoping masts are critical assets that enable reliable and flexible operations. Their ability to extend and retract repeatedly, while supporting variable loads, makes them indispensable tools for professionals working at height or in remote environments. However, sustaining longevity and peak performance requires not just careful operation, but also diligent maintenance. For those interested in more advanced options, a telescoping drilling rig mast with hydraulic jacking system offers robust performance for challenging applications and vigorous operational cycles.
When neglected, even the highest quality telescoping masts can quickly succumb to problems such as corrosion, grit buildup, or mechanical failure. Addressing these risks proactively ensures the mast remains safe and fully functional, often far beyond its expected service life. By following tried-and-true care routines, users maximize their investment and minimize costly downtime or emergency replacements.
To maintain safety and ensure reliable operation, understanding the fundamentals of telescoping mast care should be a priority for all users, whether for occasional field deployment or daily industrial use. By investing in regular maintenance, operators not only secure uninterrupted service but also better protect personnel and valuable equipment during critical tasks.
Routine, preventative maintenance also plays a crucial role in upholding industry standards and regulatory requirements. Well-cared-for masts operate far more efficiently, reducing unnecessary strain, energy waste, and long-term costs—an especially important consideration for organizations with tight budgets or critical operations.
Table of Contents
Regular Cleaning and Lubrication
One of the most important steps in mast maintenance is minimizing friction and corrosion by keeping the mast clean and lubricated. Accumulated dirt and grime can wear down moving parts, causing the mast to jam, operate unevenly, or emit unwanted noise. For pneumatic masts in particular, monthly cleaning and lubrication are common practices, although you may need to adjust this frequency based on local dust levels and the frequency of mast use. Telltale signs that a mast needs care include sticking during extension/retraction, a gritty film on mast sections, or audible squeaking or grinding.
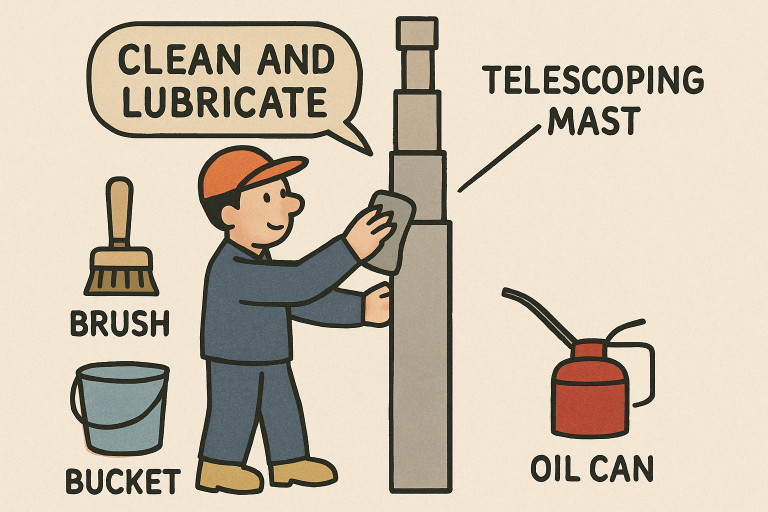
Use appropriate cleaners and lubricants—never harsh chemicals or abrasive pads—and ensure you thoroughly wipe away residue to prevent attracting more dirt. According to a guide from Popular Mechanics, regular maintenance of mechanical components is vital for preventing breakdowns and costly repairs.
Routine Inspections
Routine visual and mechanical checks are crucial for detecting small issues before they develop into major failures. When inspecting, focus on the mast’s joints, base, guy wires, cable systems, and extension mechanisms. Assess for rust, cracks, loose bolts, and binding pulleys or winches. It’s also important to inspect the mast for proper alignment, as misalignment can place untold stress on telescoping sections and supporting hardware.
Document your inspections to track wear patterns over time, and adopt a strict schedule to ensure nothing is overlooked. In particularly corrosive environments, such as near saltwater or chemical plants, increase inspection frequency and pay special attention to protective coatings.
Environmental Considerations
Exposure to moisture, salty air, extreme temperatures, and ultraviolet rays can be particularly damaging to the surface and mechanical integrity of a telescoping mast. Weather-resistant protective covers act as a first line of defense, guarding against rain, snow, and dust infiltration. By preventing corrosion and water ingress, these covers minimize maintenance and extend the mast’s operational lifespan. When working in coastal or industrial zones, extra vigilance against rust and corrosion is a must. For more insight into environmental care measures, consult resource guides by organizations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
Proper Storage Practices
When not in use, always store your telescoping mast in a dry, temperature-controlled indoor setting. This shields the mast from condensation, ambient moisture, and wide temperature swings—all of which can accelerate corrosion and material fatigue. Retract the mast fully before storage, and use available dust caps and top covers to prevent contaminants from entering the internal mechanisms. Masts stored outdoors should be covered with waterproof, UV-resistant tarps and elevated to prevent standing water at the base.
Addressing Wear and Tear
Even with careful maintenance, certain mast components—such as seals, fasteners, cables, and wear pads—naturally deteriorate over time. Make it a practice to check these frequently, replacing them at the first sign of visible wear or mechanical instability. Neglecting to do so can jeopardize the mast’s structural integrity and lead to unexpected failures during use. Keeping spare parts on hand and maintaining a log of previous repairs streamlines this process and prevents unnecessary downtime in the field.
Adhering to Manufacturer Guidelines
Every telescoping mast model is designed with specific materials, coatings, and tolerances. Always consult and follow the maintenance recommendations and safety instructions provided by your mast’s manufacturer. These guidelines are tailored to the unique requirements of your equipment, ensuring best practices are followed for lubrication types, adjustment torque, and recalibration intervals. Thorough record-keeping and strict adherence to manuals support warranty claims and liability protection.
Training and Safety Measures
Only properly trained personnel should handle the operation, maintenance, and repair of telescoping masts. Comprehensive training minimizes the risk of accidents, improper adjustments, and equipment misuse. In addition to skill instruction, reinforce the use of personal protective equipment and safety barriers during hands-on mast work. Observe lockout and tagout protocols before servicing mechanical or electrical systems to minimize the risk of further danger.
Final Thoughts
Telescoping masts are major investments that, with proper care, can provide years—even decades—of reliable service. Consistent attention to cleaning and lubrication, regular inspections, proactive storage, and timely component replacement form the backbone of a successful maintenance program. By prioritizing well-documented preventative care and adhering to professional guidelines, organizations ensure they maximize uptime, protect operators, and get the most out of their telescoping mast assets.